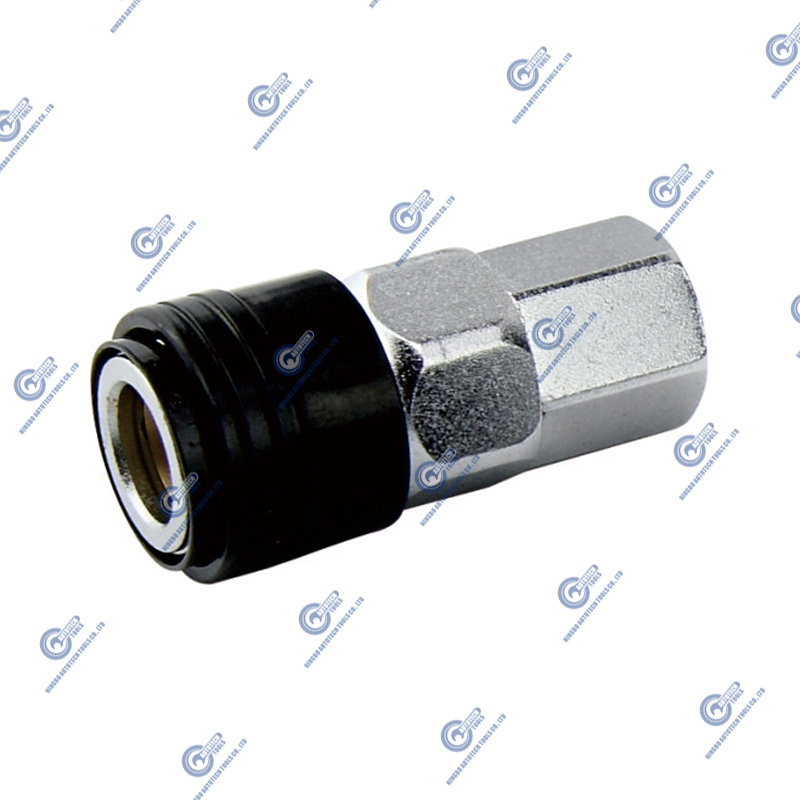
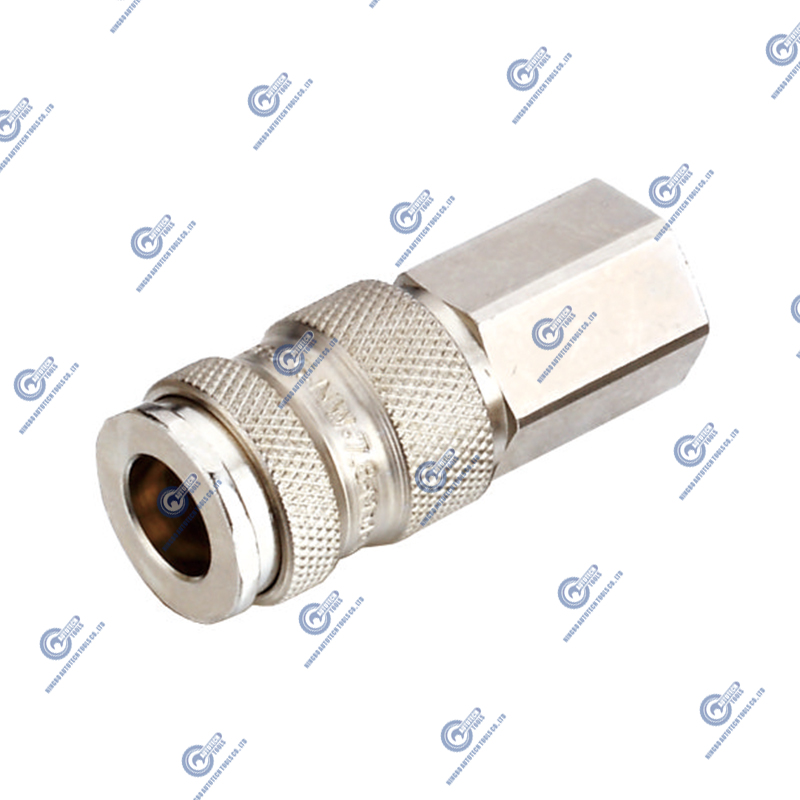
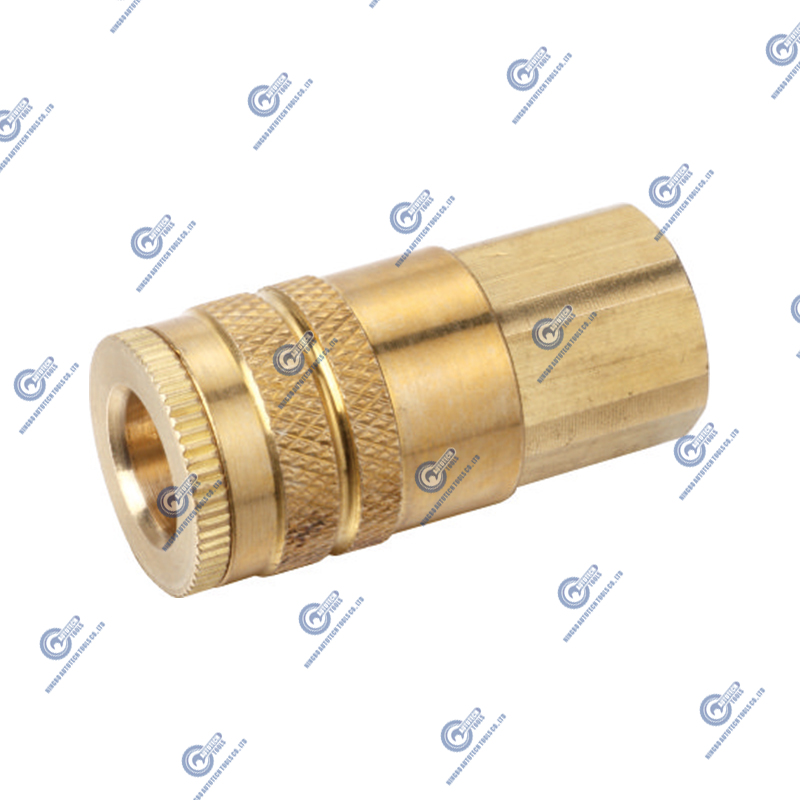
Life Testing of Air Couplers and Plugs by Fatigue Testing
 2024.09.25
2024.09.25
 Industry news
Industry news
Fatigue testing is an important method to evaluate the reliability and durability of air couplers and plugs in long-term use. Since air couplers and plugs are frequently connected and disconnected in pneumatic systems, their design and material selection must be able to withstand repeated mechanical stress and pressure fluctuations.
The implementation of fatigue testing usually includes the following steps:
Sample preparation: Prepare multiple air coupler and plug samples of the same specifications to ensure the repeatability of the test results. The samples should use the same materials and manufacturing processes as the actual application.
Test equipment: Use a fatigue testing machine, such as a servo-controlled fatigue tester, that can perform repeated connection and disconnection operations at a preset pressure and frequency. The test equipment needs to be equipped with a data acquisition system to record the stress and deformation of each cycle.
Loading scheme: Determine the loading scheme for fatigue testing, including the working pressure range and the frequency of connection and disconnection. Usually, the test is carried out under conditions close to the working pressure limit to simulate a bad use environment.
Testing process: According to the set loading scheme, the connection and disconnection operations are continuously carried out, and the number of operations, stress state and any failure signs of each sample are recorded. The test continues until the sample has visible fatigue failure or reaches a preset range of cycles.
Data Analysis: After the test, the recorded data is analyzed and a stress-cycle curve is plotted to evaluate the fatigue performance and service life of the material. By comparing the fatigue life of different materials and designs, it can help optimize the design of gas couplers and plugs.















